What are the most commonly used alternatives for disinfecting treated wastewater
What are the most commonly used alternatives for disinfecting treated wastewater?
Traditionally, the use of chlorine gas was the most common method of wastewater disinfection. Chlorine gas itself is relatively inexpensive but is a highly toxic chemical that must be transported and handled with extreme caution. It is stored under pressure in large tanks and is released into the wastewater as a gas. Sodium hypochlorite is a diluted liquid form of chlorine that is also commonly used.
Today, UV disinfection is widely accepted for municipal wastewater disinfection around the world. UV is rapidly growing, given it’s a safe and cost-effective alternative over chemical disinfection. Also, it produces no disinfection byproducts or a chlorine residual, which is harmful to the environment. The UV disinfection process adds nothing to the water but UV light, and therefore, has no impact on the chemical composition of the water.
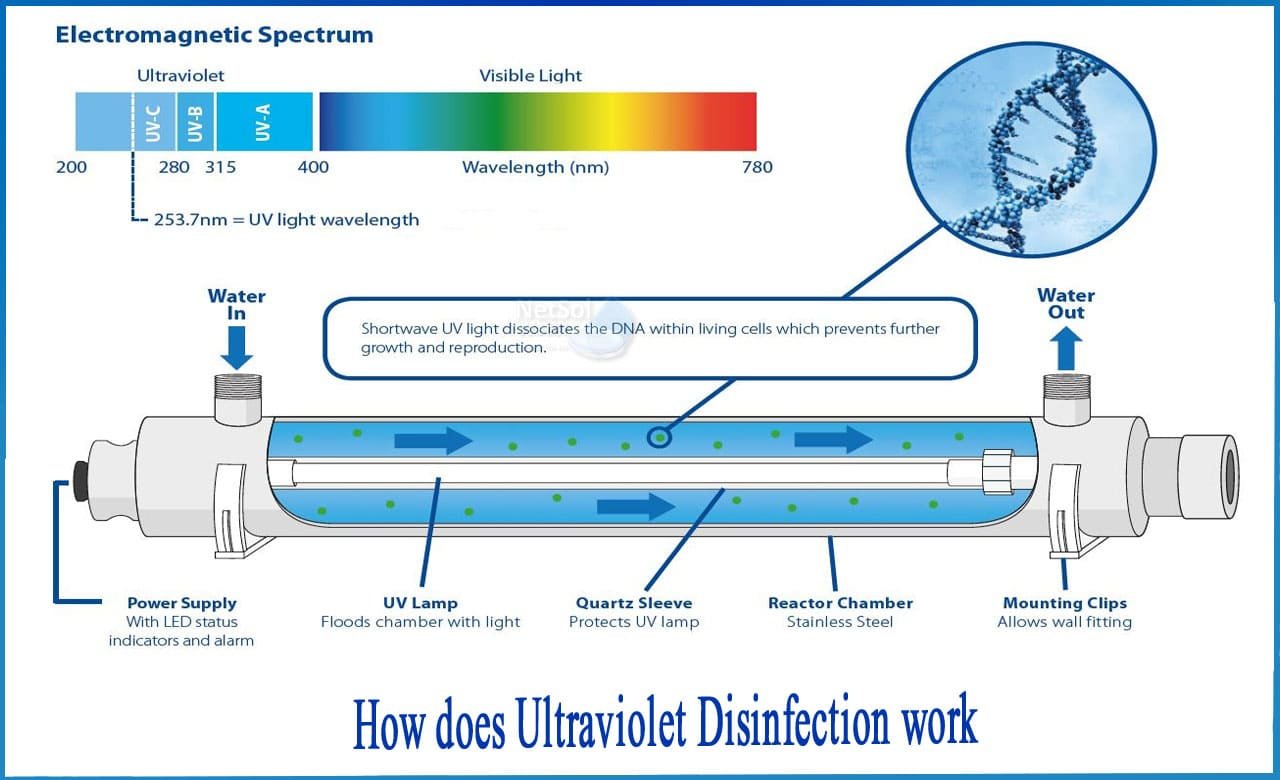
How effective is UV at destroying pathogens, as compared to chemical disinfection methods?
UV is a very cost-effective and a reliable technology that protects the public against pathogenic microorganisms, including protozoa, bacteria and viruses. Chemical disinfection using chlorine is also effective against these pathogens; however, there are pathogens, such as Cryptosporidium and Giardia, which are chlorine-resistant but can be disinfected by UV light.
Related: Many people helped Shelly Higdon advance in her career. Now she takes time to pay it forward.
Unlike chemical approaches to water disinfection, UV provides rapid, effective inactivation of microorganisms through a physical process. The retention time required to achieve disinfection ranges from a few seconds compared to several (>30) minutes for chlorine disinfection. This eliminates the need for large chlorine contact chambers, thereby reducing the required footprint and cost of installation.
Are there any employee safety issues involved with operating a UV disinfection system?
There should be safety plans in place for any disinfection technology used. The safety risks for operating a UV system, although low, are related to operator exposure to high levels of UV light and possible electrical hazards. The exposure to UV light is very low given that UV light is shielded from operators by channel grating and “light locks.” There are lock-outs in the power cabinets as well to ensure power is off, and lock-out/tag-out occurs when servicing a UV system. As with operating and working with any type of equipment, it is recommended that proper personal protective equipment be worn and safety procedures be followed. Owners and operators of UV disinfection systems should have operational practices in place. These are generally provided in the O&M manual from the UV system supplier and cover several items, including:
- Procedure for lamp maintenance and replacement
- Procedure for monitoring the system operation
- Proper disposal of UV lamps, ballasts, quartz sleeves and other components
What types of public safety concerns are associated with the use of UV disinfection versus chlorination?
The advantage that UV disinfection is a physical process and does not alter the quality of the water also makes it a perceived disadvantage, in that it does not leave a residual for monitoring. Without a residual, there may be a concern that the UV dose is low and pathogens are not being adequately disinfected, and/or pathogens can sometimes repair and reverse the destructive effects of UV through a “repair mechanism,” known as photo reactivation, or in the absence of light known as “dark repair.”
Although these may be legitimate concerns, they can be overcome by working with a UV supplier with proper sizing tools and expertise in leading-edge controls and monitoring.
Through proper sizing, an adequate UV dose can be delivered to prevent photo reactivation. Furthermore, through incorporating a robust and calibrated UV lamp intensity sensor for dose control, the real-time UV dose for the system can be monitored and controlled to ensure continuous adequate disinfection.
Tags- UV disinfection versus chlorination, UV disinfection system, Waste Water Treatment Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, Chennai, Madurai, Kerala, Karnataka


